I had worked so hard to create the perfect situation that in the end nobody could enjoy the results. Yes, I have ruined quite a lot of things, relationships and processes. Of course with the best intentions. At work, I see bright and intelligent people trapped in similar battles. Scared to make a decision or in doubt on a solution? Point at the imperfect nature of a someone else’s solution: “this is not a total solution, so go back to the drawing board”.
The Nirvana fallacy: the lie of the perfect solution
Some years ago I called this the Nirvana fallacy. It is simple and widespread in IT way of working: you compare a solution with an ideal and not with an alternative solution. This is great for killing any initiative and keep the status quo. How inconvenient that situation may be: the solution is not perfect so we have to reject it.
A fine variant is “we have to wait for the outcome” of another project, of another meeting. Leaders should be alert and ask for an alternative way of working or an alternative solution. Yet, we run the risk that no one in the meeting is alert. This is quite convenient for the Nirvana player. He/she shows the “real” solution. He/she is quite a colleague because he/she knows what is best for the organization.
Why this fallacy works in any imperfect situation
The moment an application or hardware comes out of the box the imperfection starts. It needs to be combined with other applications, hardware and requirements. There is no manual for that combination. Since our organization is unique -that’s what most members think of their own organization- the combination is unique. And since we want the best for our organization….
Wabi-sabi: beauty within constraints
A fruitful perspective is wabi-sabi. This Japanese and buddhist concept concentrates on the beauty of everything not perfect. Individuality, authenticity and imperfection are important values in this form of art. Hey, those values sound familiar for every unique organization. Yes but, that is art, we cannot compare it to complex IT applications and processes.
Option B: a way out?
In her book Option B Sheryl Sandberg quotes a friend, promising her to deal with deep adversities: “Option A is not available”. He then promised to help her make the most of Option B. We all live some form of Option B.
Yes, but, -always this “yes but”- that is on personal life. We IT geeks work with binary stuff, good and bad, black and white, functioning and not functioning. Well, let us be fair: how many times have we said of our own work “in principle it is ready” or “normally it works”. We are quite forgiving on our own products, processes. Why not give others the same amount of credits? And improve transparently in small steps?
Metrics
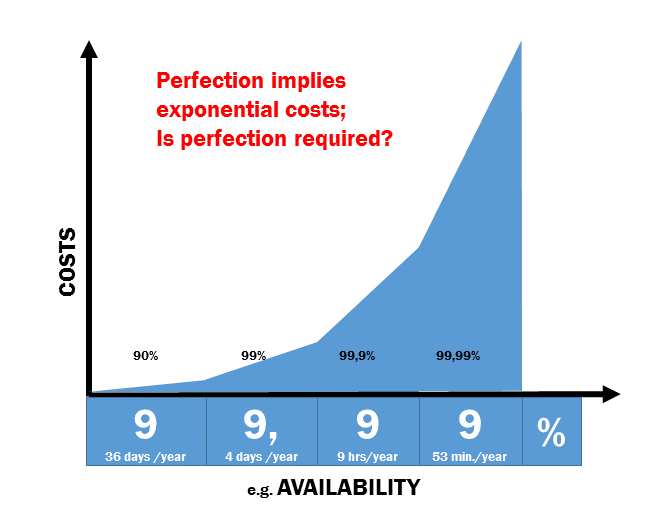
A few years ago I had to take over a project and assess the results of the developers. I was fed up with all the “in principle”, “nearly ready”, “90% ready” so I started asking whether the results could be set in production tomorrow. Additionally I requested the following answers: pregnant or not pregnant. All the green lights turned into red lights and program management freaked out. One of my present customers prefers absolute transparancy since it clarifies what needs to be done. His courage lies in transparancy, regardless of the outcomes. His power lies in clearly defined goals. I like to go further. Clearly defined goals are important but measuring the results as well. That’s what I like in Scrum:
- large scale epics are cut into smaller user stories
- only some of those smaller stories are realised in upcoming work
- previously, we had agreed upon the definition of done to assess the results
So imperfect, real curves and corners are ok, the best we want and they give way for improvement:
- ask for alternatives when confronted with the Nirvana fallacy
- accept the imperfection of your organization, yourself … and your colleagues
- create a roadmap with small, clear and measurable results
… Just do it
Some tasks paralyze us. They are big, hairy and audacious. From present innovation culture we can learn the acceptance of failure, learning from failures and failing forward. In my work I present fast to provide others with the opportunity to improve and take ownership of solutions. Just start the discussion forward with the risk of rejection and the opportunity of cooperation.
Happy hunting.

 Solution
Solution


